Key facts and figures
![facts_figures[1]](https://gmusc.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/facts_figures1.jpg)
The Global Burden of Disease 2019
A series of reports have been published in The Lancet Rheumatology in 2023 and 2024 on the burden of musculoskeletal (MSK) conditions. For a list of publications, click HERE
MSK conditions include joint diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), back and neck pain, osteoporosis and fragility fractures, soft tissue rheumatism, injuries due to sports and in the workplace, and trauma commonly related to road traffic accidents
They cause pain, physical disability and loss of personal and economic independence
-
MSK conditions affect millions of people of all ages in all cultures and in all countries
- Current estimates of people affected worldwide (Lancet Rheumatology 2022-2023)
- Back pain: 619 million
- Neck pain: 203 million
- OA: 595 million
- Other musculoskeletal conditions: 494 million
- Rheumatoid arthritis: 18 million
- Current estimates of people affected worldwide (Lancet Rheumatology 2022-2023)
-
MSK conditions are the leading cause of disability
, as measured by years lived with disability (YLDs) worldwide and across most regions of the world (IHME GBD Compare)- As a group musculoskeletal disorders cause 17.1% of all years lived with disability (YLDs)
- The main contributors are low back pain (63.7 million YLDs), neck pain (22.1 million YLDs), osteoarthritis (18.9 million YLDs) and the other musculoskeletal category (38.5 million YLDs). Osteoarthritis of the knee accounts for 35% of total OA in central Asia, to 66% in east Asia
- Of the individual conditions, low back pain is the leading cause of disability worldwide, accounting for 7.4% of total YLDs
-
MSK conditions have the fourth greatest impact on the health of the world population
, when both both death and disability are take into account (DALYs – Disability adjusted life years) (IHME GBD Compare)- Musculoskeletal disorders account for 5.9% of total global DALYs
- Low back pain accounts for 2.5% of total burden, neck pain almost 1%, and osteoarthritis about 0.75%
- Disability due to musculoskeletal disorders is estimated to have increased by 11% from 1990 – 2019 (IHME GBD Compare). Disability due to Other musculoskeletal disorders increased by 60% from 1990 to 2019 and Osteoarthritis by 48%. This relates to ageing of the population, increased obesity and lack of physical activity.
- A considerable proportion of disability due to musculoskeletal conditions can be effectively prevented by currently available interventions, such as accident and injury prevention, modern treatment of arthritis and injuries, and by rehabilitation.
- The growing burden can be controlled if priority and resources are given to ensure access to these interventions.
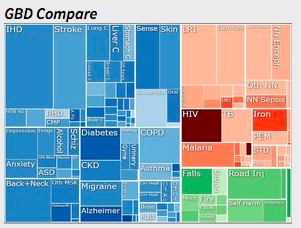
Global Burden of Disease data
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation regularly update the Global Burden of Disease data and can be found at https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/
European data
Data is available for the European countries and can be access through the following link to the eumusc.net project

Public Health England Musculoskeletal disease profile
A summary of MSK Statistics has been developed by Public Health England in collaboration with the Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Alliance (ARMA), the UK network of the Global Alliance for Musculoskeletal Health. The aim of developing this summary paper is to enable the commissioning and provision of high value MSK services in England. The summary uses data from the Public Health England Musculoskeletal disease profile tool.
The document is available at http://fingertips.phe.org.uk/profile/msk
Other countries may be interested in developing the same sort of summary to guide the delivery of high value services delivered at point of need.
USA Data
A report “Burden of Musculoskeletal Diseases in the United States” was released in the United States and can be accessed at the link below.


